SINCE 1997
DAEILPAT
Daeil Int'l Patent & Trademark Law Firm
Patent Examination
Accelerated examination system
According to Article 61 of the Patent Act, the commissioner of the Korean Intellectual Property Office may direct an examiner to examine one application in preference over another if it falls under any of the following types or circumstances:
(1) Where a person, other than the applicant, is commercially and industrially working the invention claimed in a patent application after the laying-open of the application;
(2) Where the commissioner of the Korean Intellectual Property Office deems it necessary to urgently process a patent application prescribed by Presidential Decree:
ⓐ Applications related to the defense industry;
ⓑ Applications directly related to green technology (referring to technology that minimizes emissions of greenhouse gases and pollutants by saving energy and resources and making use of them efficiently throughout the whole process of social and economic activities such as reducing greenhouse gases, raising the efficiency of energy utilization, pollution-free production, clean energy, recycling resources, and eco-friendliness (including related convergence technology));
ⓒ Applications directly related to the promotion of exportation (including the progress for adoption of international standards);
ⓓ Applications concerning the official duties of state or local governments (including any patent application concerning the duties of the national and public schools provided for in the Higher Education Act, which is filed by the organization in charge of the technology transfer and industrialization established within the national and public schools pursuant to Article 11(1) of the Technology Transfer and Commercialization Promotion Act);
ⓔ Applications filed by an enterprise confirmed as a venture business under Article 25 of the Act on Special Measures for the Promotion of Venture Businesses;
ⓔ-2 Applications filed by an enterprise selected as a technologically innovative small and medium enterprise under Article 15 of the Act on the Promotion of Technology Innovation of Small and Medium Enterprises;
ⓕ Applications concerning the results of the state's project to support the development of new technology or quality certification;
ⓖ Applications which are based on a priority claim declared under international treaties (limited to cases where a foreign patent office, upon receiving such priority claim based on the relevant patent application, is in the process of taking procedures for such patent);
ⓗ Patent-pending inventions for which the applicant is in process of commercializing the invention or is preparing to do so;
ⓘ Applications directly related to electronic transaction;
ⓙ Applications which the commissioner of the Korean Intellectual Property Office and the commissioner of a foreign intellectual property office have agreed to preferentially examine;
ⓚ Applications requesting that one of the KIPO-approved agencies (namely the Korea Institute of Patent Information; WIPS Co., Ltd; and the IP Solution Co., Ltd.) conduct a prior art search and forward the search results to the commissioner of KIPO.
An applicant desiring an accelerated examination of his/her application must submit a written request containing a statement explaining the necessity thereof in detail and any supporting evidence.
Flow chart of an accelerated examination

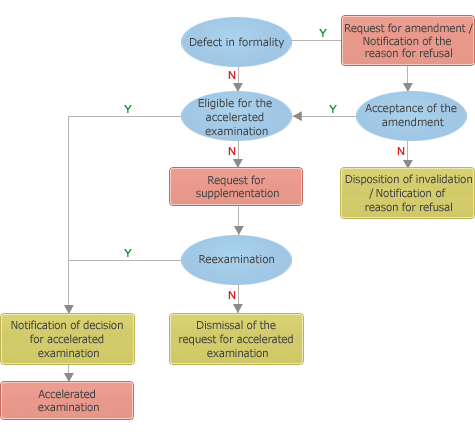
-
Deferred examination system
If necessary, applicants can request a deferred examination within nine months from the date of the examination request. The applicant can also choose the date of the deferred examination which must take place at least two years after the examination request and within five years of the application date. The applicant will receive the first office action from KIPO within three months of the deferred examination date.
-
Divisional application
An applicant who has filed a patent application comprising two or more inventions may divide the application into multiple applications.Flow chart of a divisional application
Flow chart of a divisinal application
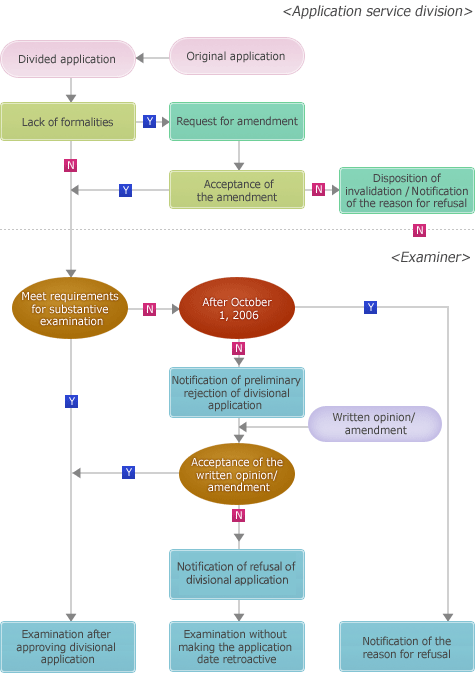
-
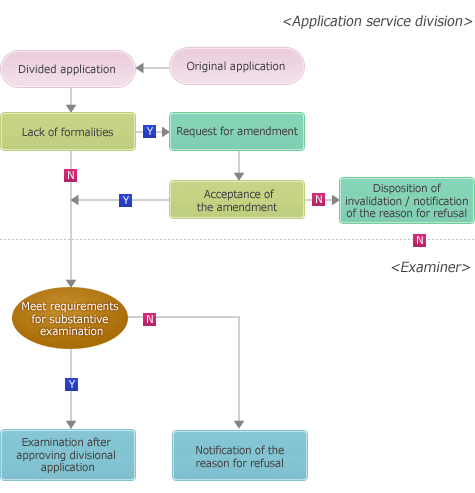
Converted application
An applicant can convert a patent application to a utility model application or vice versa within thirty days of the date on which the applicant received a certified copy of the first decision of rejection.
Flow chart of a converted application
-
Priority claim under treaty
The system of making a priority claim under treaty is recognized by the Paris Convention and by the member countries of the WTO. Whenever an application filed in one country is filed again in another member country within a year of the first filing, the filing date of the subsequent application is deemed to be the filing date stated in the original application.
Flow chart of a priority claim under treaty
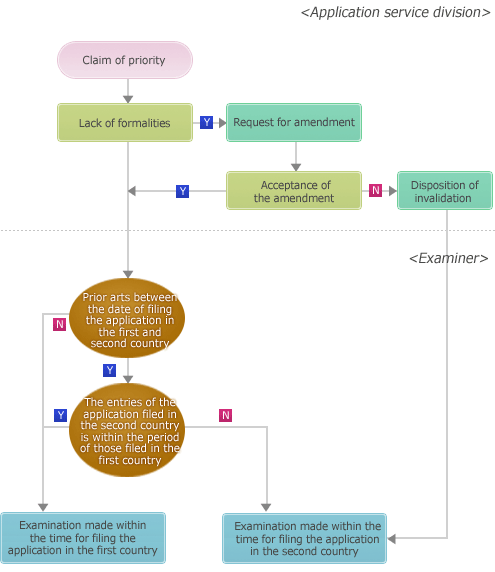
-
Claim for domestic priority
An applicant may make a priority claim based on an invention described in the specification or drawings initially attached to an earlier application of a patent or utility model registration within a year of filing the earlier application for which he/she has the right to obtain.
Flow chart of a priority claim for domestic priority
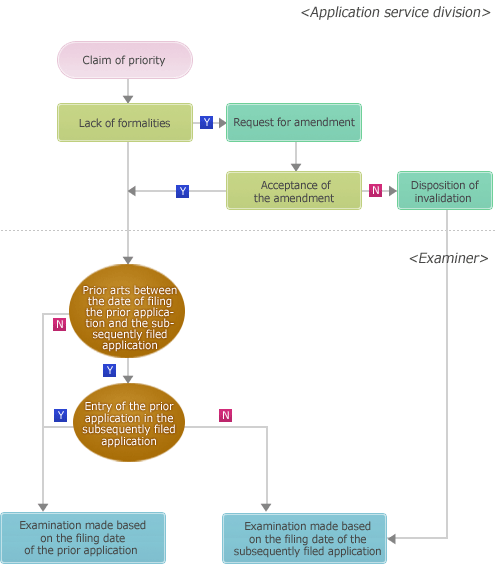
-
Ex officio amendment
If an examiner determines that an application is patentable but has any clear clerical errors in the specification, drawings, or abstract attached to a patent application such as misspellings or wrong reference numbers, the examiner can make an ex officio correction of the error without having to request the applicant submit a written opinion. (For decisions of registration made after July 1, 2009.)
-
Request for reexamination (reexamination before a trial)
Under the revised Patent Act, if an examiner rejects an application, the applicant can simply request a reexamination after amending the description or drawing(s). Previously, upon receiving a decision of refusal, an applicant had to appeal the examiner's decision and amend the description or drawing(s) for examination before a trial.
-
Flow chart of a request for reexamination (for applications filed after July 1, 2009)
① Reasons for refusal from before the date of the first decision of refusal, but were not mentioned
② Reasons for refusal which were created by the amendments made after the decision of refusal, but were not mentioned
③ Reasons for refusal mentioned in previous notice of refusal
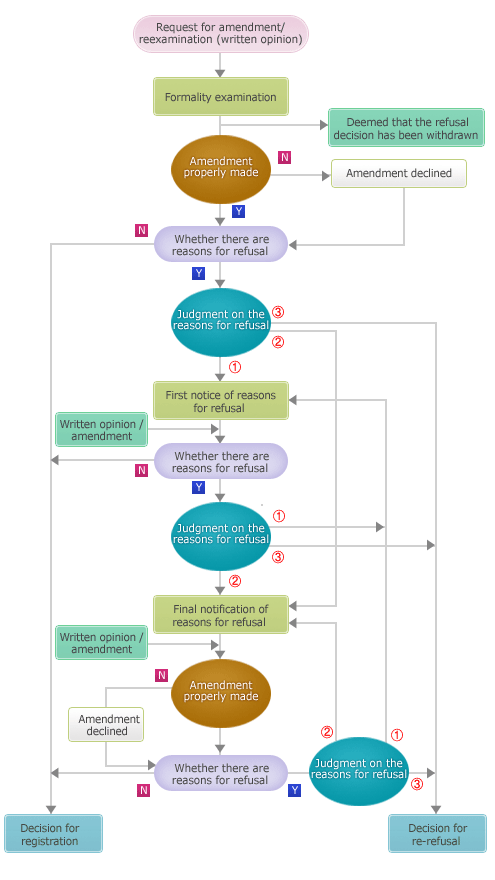
-
Flow chart of a reexamination before a trial (for applications filed before June 30, 2009, and after July 1, 2001)
① Reasons for refusal from before the date of the first decision of refusal, but were not mentioned
② Reasons for refusal which were created by the amendments made after the decision of refusal, but were not mentioned
③ Reasons for refusal mentioned in previous notice of refusal
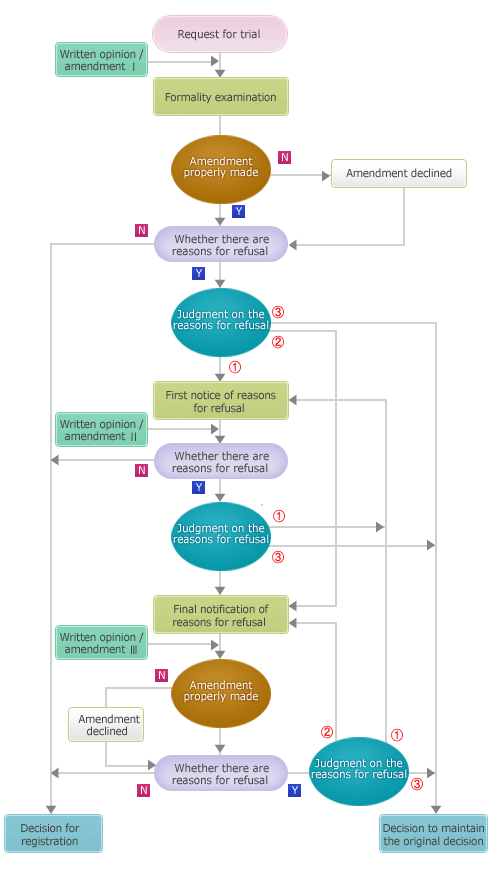
-
Pendency period
- The first office action pendency period starts when an applicant requests an examination and ends when the examination begins. A prolonged pendency period delays the enforcement of rights and hinders the commercialization and profitability of new technologies.
- To shorten the pendency period, KIPO has increased its number of patent examiners, expanded its outsourcing of prior art searches, maximized its examination capabilities through performance-based management, developed an automatic search system, and introduced Six Sigma management methods. As a result of those efforts, KIPO provides the world's fastest examination service.
-
Average first office action pendency period for patent and utility models
